Module4_Pedagogy
Pedagogy Module
Module Objectives:
- Identify and apply best practices in teaching and learning in the online environment, as informed by research.
- Identify and select instructional strategies/techniques appropriate to your online environment.
- Recognize and write well defined objectives.
- Relate QM Standards 2 to online course
Glossary of Key Terms
|

|
Asynchronous --Students do not all have to be present at the same time. Students can work at their convenience any time or place. |
|
Synchronous--Students are online at a specified time. An example is a webinar that is held live and in real time.
|
|
Face-to-Face--Also referred to as the traditional classroom. The instructor and the students are in a place, usually a classroom, devoted to instruction. The teaching and learning take place at the same time. For example, a Face-to-Face English class would meet on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday from 9 a.m. to 10 a.m. in Room 102. |
|
Hybrid--Also called blended learning, blend face-to-face interaction such as in-class discussions, active group work, and live lectures with typically web-based educational technologies such as online assignments, discussion boards, and other web-assisted learning tools.
|
|
Online--A course for which all regularly scheduled classroom time is replaced by required activities completed at distance and managed online.
|
|
Pedagogy--The function or work of a teacher; teaching. The art of science of teaching; education; instructional methods.,
|
|
Objective--Learning objectives are statements that define the expected goal of a curriculum, course, lesson or activity in terms of demonstrable skills or knowledge that will be acquired by a student as a result of instruction. Also known as Instructional objectives, learning outcomes, learning goals.
|
Online Education--What do you think?
Please rate the relevance of this video to your online instruction
Hover over the star to see the description of the rating.
Teaching Online: An Overview
Online teaching is still relatively new. So new, many people do not know what it is, how it is done, and especially some of the terminology. Some of you may know what it is, but may not know how to get started. You may also have trepidation about handling some of the issues.
Many students already use the Internet to get their work done. They use technology as a primary means of communication. In academics, we are just beginning to become familiar with these tools. Virtual classrooms can deliver lessons to students anywhere and at anytime. Online learning is flexible for students. New technologies and techniques are emerging all of the time.
If you remove your conventional classroom tools, how do you teach? Does your pedagogy completely change just because you are teaching online?

Pedagogy--Teaching and Learning Strategies
What is Pedagogy?
Pedagogy is the science and art of teaching.
Effective teachers use an array of teaching strategies because there is no single, universal approach that suits all situations. Different strategies used in different combinations with different groupings of students will improve learning outcomes. Some strategies are better suited to teaching certain skills and fields of knowledge than are others. Some strategies are better suited to certain student backgrounds, learning styles, and abilities.
Online Pedagogy--Teaching and Learning Strategies
What's different in the online classroom?
Since 2000, online education has spread rapidly across the United States and is expected to continue to grow. While the spread of online courses is important, success is dependent on the availability of trained online instructors to teach these courses.
In the virtual classroom, as in the traditional classroom, the teacher remains the single most important factor in a student's success.
As the National Education Association states in their recent Guide to Teaching Online Courses, "Good courses require good teachers. This is where the online opportunity provides the greatest opportunity, and the greatest challenge. Online teaching shares much with face to face teaching, but it also has a unique set of skills and requirements if educators are to teach well online."
Key Differences in the Online Classroom
Move your mouse over each key difference to read more information.
|

|
Online curriculum is different from face-to-face curriculum.
|
|
Social dynamic is different in an online classroom.
|
|
Assessment strategies are different in an online classroom.
|
Traditional vs. Online
Do not be discouraged when you read that teaching online is different. Different doesn't always have to be negative. Of the many instructional strategies available for use in the online learning environment, most have not been developed specifically for online instruction, but are currently used in traditional classrooms, and can be successfully adapted for facilitating online learning. Educators should choose instructional strategies that are most effective for accomplishing a particular educational objective. From this perspective, instructional strategies are tools available to educators for designing an online course and to facilitate learning . Below are ten instructional strategies which have been effectively used in the traditional classroom and can likewise be used in the online learning environment: Hover over each strategy to learn more information.
|
Strategies used in both the traditional classroom and online. Hover over the activity for additional information.
|
|

|
Learning Contracts |
Small Group Work |
| Discussion |
Project |
| Lecture |
Collaborative Learning |
| Self-Directed Learning |
Case Study |
| Mentorship |
Forum |
A New Pedagogy is Emerging....And Online Learning is a Key Contributing Factor
The benefits and challenges of online learning are at the fore front for 21st century educators.
Perhaps the most important issues concerning education is how technology is changing the way we teach, and more importantly, the way students learn.
Three Emerging Pedagogical Trends
Underlying these developments are some common factors or trends:
- A move to opening up learning, making it more accessible and flexible. The classroom is no longer the unique centre of learning, based on information delivery through a lecture.
- An increased sharing of power between the professor and the learner. This is manifest as a changing professorial role, towards more support and negotiation over content and methods, and a focus on developing and supporting learner autonomy. On the student side, this can mean an emphasis on learners supporting each other through new social media, peer assessment, discussion groups, even online study groups but with guidance, support and feedback from content experts.
- An increased use of technology not only to deliver teaching, but also to support and assist students and to provide new forms of student assessment.
Pedagogy Learning Tab Activity
A New Pedagogy Developing
What are some key elements contributing to the development of this new pedagogy?
Best Practices in Online Teaching and Learning
Research shows us that certain elements must be present in an online course and included as part of the Online Teaching and Learning strategy. These Best Practices are like pieces of a puzzle. The puzzle is best when all pieces fit in the correct place. If pieces are missing, the puzzle is not complete. If pieces are forced in an incorrect place, the puzzle is not complete. Look at this illustration below. Have you incorporated these practices represented as puzzle pieces as part of your online teaching strategy?
Learning Goals and Learning Objectives
|

|
Every program of instruction, course, or training activity begins with a goal.
This goal can be broken down into specific goals, or learning objectives, which are concise statements about what students will be able to do when they complete instruction.
|
What's the difference between a learning goal and a learning objective?
Learning Goals are what you hope to accomplish in your course: the overall goals that do not necessarily result in products of observable and measurable behavior.
Learning Objectives are brief, clear statements about what students will be able to do when they complete instruction
Why are learning objectives important?
They guide your choices. The philosopher Seneca once said, "If one does not know to which port one is sailing, no wind is favorable." When you know where you are headed, you can more easily get there.
.Well-defined and articulated learning objectives are important because they:
- provide students with a clear purpose to focus their learning efforts
- direct your choice of instructional activities
- guide your assessment strategies
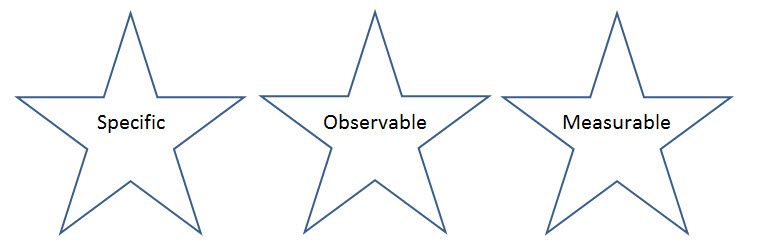
Learning Objectives that Shine
What do good learning objectives need to be? Specific, observable, and measurable
|

|
The most important and challenging aspect of writing good learning objectives is defining observable behavior that can be measured. "Learning" and "understanding" are laudable instructional goals, but they are not observable or measurable. You cannot measure learning or understanding; but you can measure how well a student can organize, label, explain, or create.
|
Learning Objective Elements
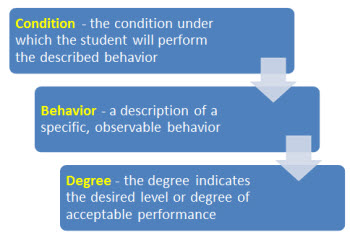
What do I include in the learning objective? condition, behavior, and degree
Well-written learning objectives include these three elements:
Let's look at an example:
|
If the students should be able to do this:
|
The learning objective would be:
|
|
Example:
|
Condition
|
Behavior
|
Degree
|
|
HISTORY
|
|
|
|
|
Illustrate the differences between early American presidents
|
Using course notes and other references
|
Create a diagram to compare and contrast the ideology and political characteristics of two early American presidents
|
With at least 5 characteristics for each president from the Encyclopedia Britannica
|
Bloom's Taxonomy
What is Bloom's Taxonomy? A classification system of thinking and learning
Benjamin Bloom was an educational theorist and teacher who studied the nature of thinking. His taxonomy has been widely used in the field of education since the 1950's.
Bloom's Levels from simple (concrete) to complex (abstract) include: remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating.
As you look at the diagram, use your mouse to hover over the different colorful pieces. On the actual puzzle, we have listed the Bloom's levels. The text popper includes action verbs that should be used in your learning objective.
Bloom's Action Verbs
Concrete verbs such as "identify," "argue," or "construct" are more helpful than vague or passive verbs ("understand" or "know" or "be aware of"), to articulate clear learning goals, and to guide the design of assignments and activities as well as assessment.
Below are examples of action words frequently used for learning objectives.
|
Knowledge
|
Comprehension
|
Application
|
Analysis
|
Synthesis
|
Evaluation
|
|
Define
|
Classify
|
Apply
|
Analyze
|
Arrange
|
Appraise
|
|
Identify
|
Describe
|
Compute
|
Appraise
|
Assemble
|
Assess
|
|
Indicate
|
Discuss
|
Construct
|
Calculate
|
Collect
|
Choose
|
|
Know
|
Explain
|
Demonstrate
|
Categorize
|
Compose
|
Compare
|
|
Label
|
Express
|
Dramatize
|
Compare
|
Construct
|
Contrast
|
|
List
|
Identify
|
Employ
|
Contrast
|
Create
|
Decide
|
|
Memorize
|
Locate
|
Use
|
Criticize
|
Design
|
Estimate
|
|
Name
|
Paraphrase
|
Illustrate
|
Debate
|
Formulate
|
Evaluate
|
|
Recall
|
Recognize
|
Interpret
|
Determine
|
Manage
|
Grade
|
|
Record
|
Report
|
Investigate
|
Diagram
|
Organize
|
Judge
|
|
Relate
|
Restate
|
Operate
|
Differentiate
|
Perform
|
Measure
|
|
Repeat
|
Review
|
Organize
|
Distinguish
|
Plan
|
Rate
|
|
Select
|
Suggest
|
Practice
|
Examine
|
Prepare
|
Revise
|
|
Underline
|
Summarize
|
Predict
|
Experiment
|
Produce
|
Score
|
|
|
Tell
|
Schedule
|
Inspect
|
Propose
|
Select
|
|
|
Translate
|
Shop
|
Inventory
|
Set up
|
Value
|
|
|
|
Sketch
|
Question
|
|
|
Bloom's Taxonomy According to Andy Griffith
Please rate the relevance of this video to your online instruction
Hover over the star to see the description of the rating.
Get started on the Right Foot

Everyone have writers block. You know what you want to say. You just need a little help getting started. Check out the Guidelines Below. Keep a copy handy as you continue on to the various other Modules of the course.
Guidelines for Stating Learning Objectives
"[Learning] objectives should be stated in terms of what learners will be able to know, do, or feel. Objectives should consist of an opening statement ('The student will…'), an action verb, and a content reference (which describes the subject being taught)… the three essential elements of all learning objects are a statement of who (the learner), how (the action verb), and what (the content)."
|
Learner
|
Action Verb
|
Content
|
|
The participant will.....
|
DESIGN
|
?
|
|
The student will.....
|
ANALYZE
|
???
|
|
The learner will.....
|
EXPLAIN
|
?????
|
Self-Check Activity
Use this activity as a review of Bloom's Taxonomy. Drag the Bloom's level to match the definition. The tile will only fit in the correct spot. You may wish to try this activity more than once.
Online Pedagogy Resources

Face-to-face teaching relies on visual and aural clues. In the online environment, we have to use different strategies to insure effective teaching and learning. The information below presents pedagogical strategies for thinking about teaching and learning in an online environment.
Online Pedagogy Resources
http://teach.ucf.edu/pedagogy/bestpractices/
http://www2.ed.gov/rschstat/eval/tech/evidence-based-practices/finalreport.pdf
http://www.npr.org/2011/07/14/137853462/rethinking-how-we-teach-the-net-generation?ft=1&f=1049
http://jolt.merlot.org/vol6no1/dell_0310.htm
http://jolt.merlot.org/vol5no4/degagne_1209.htm
Commonly Asked Questions by Students
|

|
Students who enroll in an online class for the first time often are unclear about what to expect in these new forms of courses. Below, please find some answers to frequently asked questions about hybrid or online classes.
|
Source:
Frequently Asked Questions created by Dr. Marsha Conley, Instructional Technology Coordinator at American River College
Self Evaluation for Online Students
|
Consider using this resource for students.
This quiz was written by the Illinois Online Network and was originally intended for Potential Online Students. However, it could easily be adapted to use in your online course.
You may also want to pull a few of the questions for your discussion topics.
|

|
Check out the online version at: http://www.ion.uillinois.edu/resources/tutorials/pedagogy/selfEval.asp
Reflection
A Vision of Today's Student
Below is a short video summarizing some of the most important characteristics of students today: how they learn, what they need to learn, their goals, hopes, dreams, what their lives will be like, and what kinds of changes they will experience in their lifetime.
This video was created by Michael Wesch in collaboration with 200 students at Kansas State University.
video time: 4:45 min
Please rate the relevance of this video to your online instruction
Hover over the star to see the description of the rating.
Conclusion
You have successfully completed the Module 4 Pedagogy lesson module.
Apply the knowledge learned in the lesson module by completing activities, assignments, discussions, reflections, and/or feedback evaluations located in the Moodle course.













